Encryption
Encryption
In cryptography, encryption is the process of encoding information. This process converts the original representation of the information, known as plaintext, into an alternative form known as ciphertext. Ideally, only authorized parties can decipher a ciphertext back to plaintext and access the original information. Encryption does not itself prevent interference but denies the intelligible content to a would-be interceptor.
For technical reasons, an encryption scheme usually uses a pseudo-random encryption key generated by an algorithm. It is possible to decrypt the message without possessing the key but, for a well-designed encryption scheme, considerable computational resources and skills are required. An authorized recipient can easily decrypt the message with the key provided by the originator to recipients but not to unauthorized users.
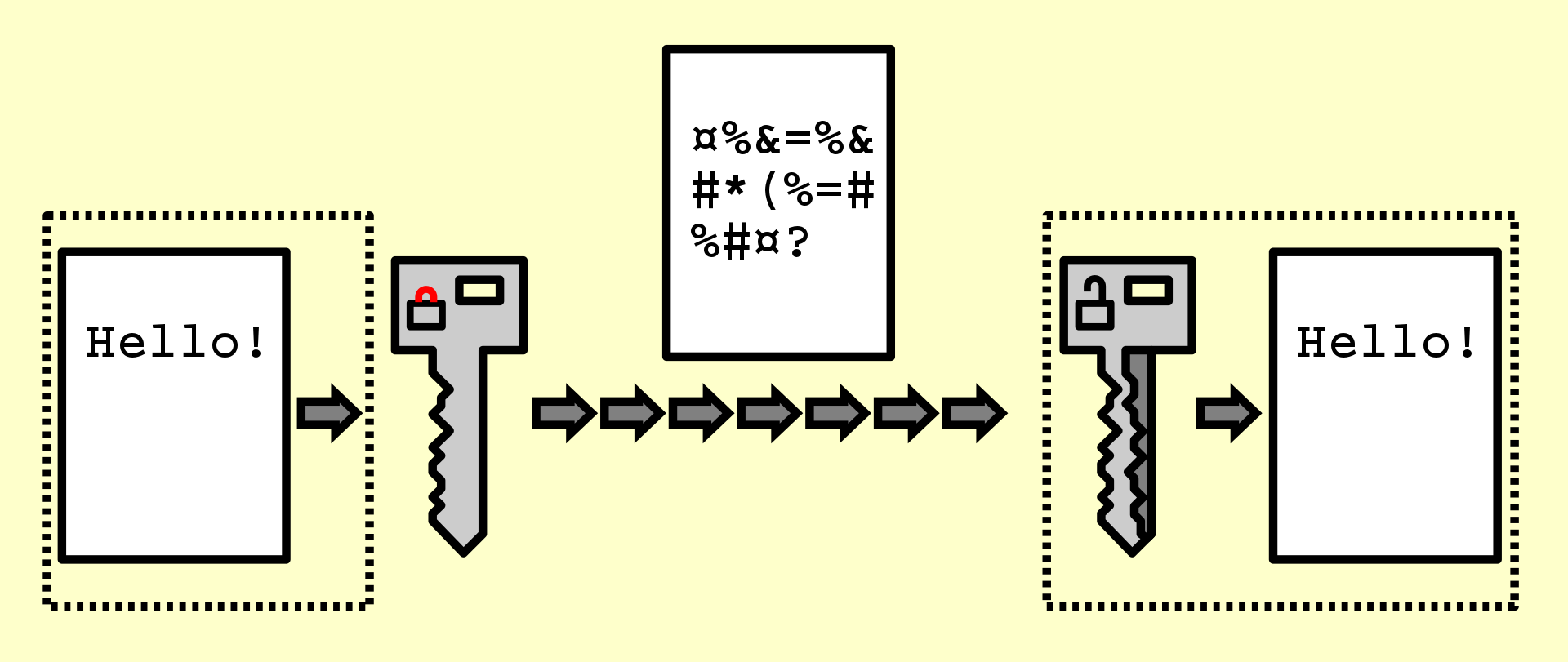
Historically, various forms of encryption have been used to aid in cryptography. Early encryption techniques were often used in military messaging. Since then, new techniques have emerged and become commonplace in all areas of modern computing. Modern encryption schemes use the concepts of public-key and symmetric-key. Modern encryption techniques ensure security because modern computers are inefficient at cracking the encryption.
Today, encryption is used in the transfer of communication over the Internet for security and commerce. As computing power continues to increase, computer encryption is constantly evolving to prevent eavesdropping attacks. With one of the first “modern” cipher suites, DES, utilizing a 56-bit key with 72,057,594,037,927,936 possibilities being able to be cracked in 22 hours and 15 minutes by EFF’s DES cracker in 1999, which used a brute-force method of cracking. Modern encryption standards often use stronger key sizes often 256, like AES(256-bit mode), TwoFish, ChaCha20-Poly1305, Serpent(configurable up to 512-bit). Cipher suites utilizing a 128-bit or higher key, like AES, will not be able to be brute-forced due to the total amount of keys of 3.4028237e+38 possibilities. The most likely option for cracking ciphers with high key size is to find vulnerabilities in the cipher itself, like inherent biases and backdoors. For example, RC4, a stream cipher, was cracked due to inherent biases and vulnerabilities in the cipher.
Reference
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Encryption
การเข้ารหัสลับ (encryption)
เป็นการเปลี่ยนรูปแบบของระบบการอ่านที่เป็นภาษาอัตโนมัติให้เป็นภาษาเครื่องหรือสัญญาณอื่น โดยเกี่ยวข้องกับวิธีการทางคณิตศาสตร์
จุดประสงค์
- ข้อมูลการเข้ารหัสเป็นความลับ เพื่อให้ยากต่อการเข้าถึงข้อมูล
- มีความสมบูรณ์ในการเข้ารหัส เพื่อให้มีความครบถ้วนในการส่งให้ผู้รับ ได้รับข้อมูลที่ถูกต้องตามที่ผู้ส่งเข้ารหัสมา
- หากเกิดความเสียหายยังคงสามารถเข้ารหัสได้ เพื่อให้มีความทนทานและยากต่อการปลอมแปลง
- ป้องกันการปฏิเสธ เพื่อป้องกันการแอบอ้างและปลอมแปลง
รูปแบบการเข้ารหัสลับ
รูปแบบการเข้ารหัสลับมีการใช้มากมายหลายแบบแต่มีรูปแบบที่ต้องใช้เป็นการแปลงสภาพของรหัสที่ไม่สามารถใช้งานได้ให้กลับมาเป็นภาษาอัตโนมัติที่เป็นได้ทั้งตัวเลขและตัวอักษรตามสิ่งที่ได้ตั้งใว้
การเข้ารหัสลับ
การเข้ารหัสลับเป็นการนำ ภาษาอัตโนมัติที่เป็นทั้งตัวเลขและ ตัวอักษรให้กลับไปเป็นภาษาเครื่องหรือสัญลักษณอื่น เช่น แปลงตัวเลขเป็นรูปภาพ ตัวอักษร หรือลายเส้นบางประเภท เป็นการแปลงด้วยเครื่องมือบ้างประเภท หรือเทียบได้เป็น แม่กุญแจ
การถอดรหัสลับ
การถอดรหัสลับเป็นการนำข้อมูลที่ได้รับการเข้ารหัสลับ มาถอดด้วยโปรแกรมภาษาอัตโนมัติที่เป็นแบบเดียวกันหรือรูปแบบการคำนวณชนิดเดียวกันมาใช้ ถือได้ว่าเป็นแม่กุญแจต้องมีลูกกุญแจที่เป็นแบบเดียวกันเท่านั้นจึงจะสามารถ ถอดแม่กุญแจออกมาเป็นภาษาซีได้
รุปแบบการเข้ารหัสลับแบบสัญญาณ
สัญลักษณะ
- การแปลงแบบภาษาระดับเดียวกันตรงกันข้าม คือ การนำอักษรหรือตัวเลขมาสลับกันในการปรับข้อความ
- การแปลงแบบขนาน เป็นการแปลงแบบระดับเดียวกัน เช่น
- การแปลง ภาษาอัตโนมัติเป็นคำสั่งซีพียู
- การแปลง ตัวอักษรในซีพียูเป็นถอดรหัสคอม
สัญญาณค้นคว้า
- การแปลงจากภาษาอัตโนมัติเป็นระบบสั่งการคอมพิชเชอร์คอมค้นคว้า
- การแปลงสัญญานมีคุณเป็นส่วนรักษาบำรุงปลูกถ่ายขับซ่อมแซมเสริมให้มนุษย์
อ้างอิง
https://th.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E0%B8%81%E0%B8%B2%E0%B8%A3%E0%B9%80%E0%B8%82%E0%B9%89%E0%B8%B2%E0%B8%A3%E0%B8%AB%E0%B8%B1%E0%B8%AA
https://aws.amazon.com/th/what-is/cryptography/